Human Resource Planning and forecasting
Human Resource Planning (HRP) and Forecasting
Human resource planning is the process of analyzing and forecasting the need for and supply of human resources in an organization. It ensures that the organization has the right number of employees, with the right skills, at the right time.
Objectives of HRP
- To ensure optimum utilization of human resources.
- To forecast future manpower needs.
- To bridge the gap between current and future HR needs.
- To develop a skilled and talented workforce.
Process of HR Planning:
- Analyzing Organizational Objectives
- Inventory of Current Human Resources
- Forecasting Demand and Supply of Human Resources
- Identifying Manpower Gaps
- Formulating HR Action Plans (recruitment, training, etc.)
- Monitoring and Control
HR Forecasting
Forecasting involves predicting future human resource requirements to avoid talent shortages or surplus.
Types of HR Forecasting
- Demand Forecasting: Estimating future HR needs based on business goals.
- Supply Forecasting: Estimating the availability of internal and external talent.
Dimensions of HR Planning
1. Quantitative Dimensions
These focus on numbers and measurable data.
2. Qualitative Dimensions
These focus on the quality, skills, and potential of employees.
Both quantitative and qualitative dimensions are crucial for effective Human Resource Planning. Quantitative analysis helps determine the number of employees needed, while qualitative analysis ensures the right quality and capability of employees are available to meet organizational goals.
HR Demand Forecasting
HR demand forecasting is the process of estimating the future human resource requirements in terms of number, skills, and positions needed to achieve organizational goals.
Methods and Techniques of HR Demand Forecasting
Database for Manpower Forecasting
A database is essential for storing and analyzing past and present employee data to make future HR forecasts more accurate.
Key Components of the Database
HR demand forecasting uses qualitative (judgment-based) and quantitative (data-based) techniques to ensure that the organization has the right people, at the right time, with the right skills. A well-maintained database supports accurate forecasting by providing reliable and updated HR data.
Recruitment and Selection Analytics
Recruitment and selection analytics refers to using data and analytical methods to improve hiring decisions by evaluating the effectiveness and fairness of the selection process.
1. Evaluating Reliability and Validity of Selection Models
Types of Validity
- Content Validity—Does the test cover all aspects of the job?
- Construct Validity—Does the test measure the right qualities (e.g., intelligence, communication)?
- Criterion-related Validity— Is there a correlation between test scores and job performance?
Example: A sales aptitude test is valid if high scorers become successful salespersons.
2. Finding Out Selection Bias
What is Selection Bias?
Selection bias occurs when the hiring process unfairly favors or discriminates against a certain group (e.g., gender, age, ethnicity) based on irrelevant factors.
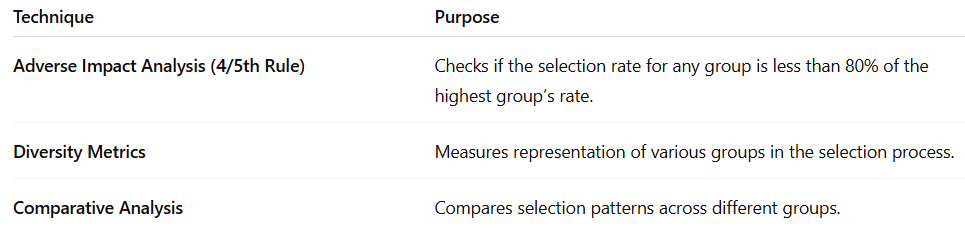
How to Detect Bias
3. Predicting Performance and Turnover
Predictive Analytics in Selection: Uses data to estimate how likely a candidate is to succeed in the role and stay in the company.
Techniques Used
- Regression Analysis—To predict job performance based on variables.
- Machine Learning Models—Analyze large datasets to identify patterns and top performer profiles.
- Retention Scores—Based on historical data to predict how long a candidate might stay.
Recruitment and selection analytics help in building a fair, data-driven, and efficient hiring process. Evaluating reliability and validity improves the quality of tools used. Detecting selection bias promotes fairness, and using predictive analytics for performance and turnover helps organizations hire the right people and reduce costs.