Contemporary Issues
Contemporary Issues in HR
1. Potential Appraisal: Potential Appraisal is the process of identifying employees' future capabilities and readiness for higher responsibilities.
Contemporary Issues
- Subjectivity: Bias in assessing potential based on past performance.
- Lack of Standard Tools: Many firms lack structured methods for future potential evaluation.
- Technology Adoption: AI and predictive analytics are now being used to assess potential more objectively.
- Employee Expectation Mismatch: If appraisal results are not used for career development, employees lose trust.
2. Competency Mapping: A process of identifying the key competencies (knowledge, skills, abilities, behaviors) required for a role and matching them with those possessed by employees.
Contemporary Issues
- Dynamic Job Roles: Rapid changes in job roles due to technology make static competency maps obsolete.
- Customization Challenge: Different roles require unique competency frameworks—one-size-fits-all doesn’t work.
- Integration with HR Systems: Linking competency data with performance appraisal, training, and hiring systems is often missing.
- Employee Resistance: Mapping can be seen as monitoring or surveillance if not communicated properly.
Linkage with Career Development
Both Potential Appraisal and Competency Mapping are vital tools in Career Development Planning, helping employees:
- Identify their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Understand promotion or growth opportunities.
- Align their personal goals with organizational goals.
Trends & Challenges
- Personalized Learning Paths: Mapping results should feed into targeted training plans.
- Lack of Follow-Up: Mapping without career development programs leads to low motivation.
- Employee Engagement: Linking competencies with meaningful career paths boosts retention.
Succession Planning
Succession Planning is a strategic process to identify and develop internal people to fill key leadership positions in the future.
Linkages
- Potential Appraisal helps identify high-potential employees for leadership roles.
- Competency Mapping ensures successors possess the right skills for future roles.
Contemporary Issues
- Lack of Prepared Talent Pool: Many firms don’t prepare successors in advance.
- Short-Term Focus: Succession often becomes reactive, not proactive.
- Bias & Favoritism: Lack of transparency in choosing successors demotivates others.
- Technology Integration: AI can predict leadership readiness and recommend development paths.
Summary Table
Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and performance management
tool developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton in the early 1990s.
Purpose
It helps organizations translate their vision and strategy into a set of
performance measures across multiple perspectives—not just financial.
Four Key Perspectives
1. Financial Perspective
- How do we look to shareholders?
- Metrics: ROI, revenue growth, profit margins.
2. Customer Perspective
- How do customers see us?
- Metrics: Customer satisfaction, retention, market share.
3. Internal Business Process Perspective
- What must we excel at?
- Metrics: Process efficiency, cycle time, quality control.
4. Learning and Growth Perspective
- How can we continue to improve and create value?
- Metrics: Employee training, skill development, innovation.
Applications of Balanced Scorecard
Advantages of Balanced Scorecard
Limitations of the Balanced Scorecard
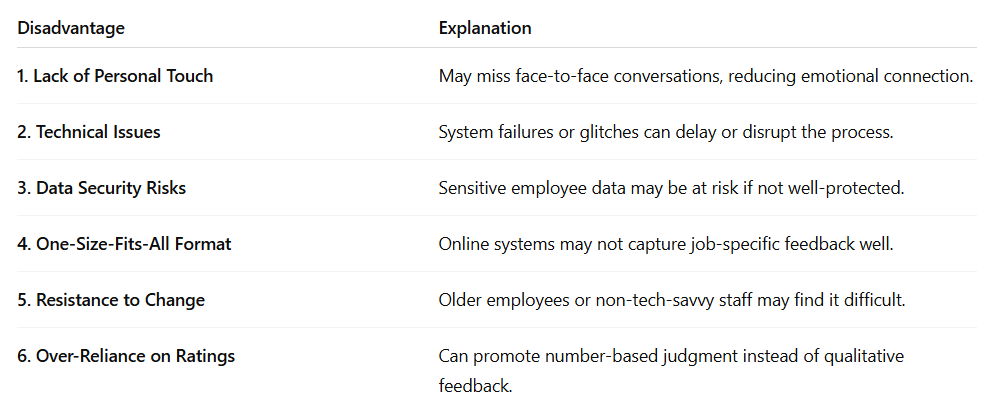
Online Appraisal
Online Appraisal refers to the use of digital platforms or software to
assess employee performance. It includes filling online appraisal forms,
giving feedback, tracking performance, and generating reports—often in
real time.