Unit 3: Foreign Exchange Transactions
Foreign Exchange Transactions
Foreign exchange transactions involve buying or selling foreign currencies for local currency (like INR) between banks, businesses, or individuals.
Types of Forex Transactions
Example: An importer purchases USD from a bank by paying rupees. , An exporter sells USD to a bank to receive rupees.
Exchange Quotations
An exchange quotation refers to how one currency is priced in terms of another.
Types of Exchange Quotations
In India: Direct Quotation is commonly used (e.g., 1 USD = ₹82).
Formula
Two-Way Quotation (Bid-Ask Spread)
Banks quote two exchange rates:
- Bid Rate: Rate at which the bank buys foreign currency.
- Ask (Offer) Rate: Rate at which the bank sells foreign currency.
Example: 1 USD = ₹81.80 / ₹82.20 , ₹81.80 → Bank buys USD from you (Bid). , ₹82.20 → Bank sells USD to you (Ask).
Why Two-Way Quotes?
- It allows banks to earn profit from the spread (Ask – Bid).
- Ensures liquidity and efficiency in forex markets.
Summary Table
Spot and Forward Transactions
Example:
- Spot: An importer buys USD on 24 July 2025 for immediate payment.
- Forward: An importer agrees today (24 July) to buy USD on 24 August 2025.
Forward Margin
Forward Margin is the difference between the forward rate and the spot rate.
Formula
Types
Purpose of Forward Margin:
- To hedge foreign exchange risk.
- Helps importers/exporters lock in rates and avoid losses from rate fluctuations.
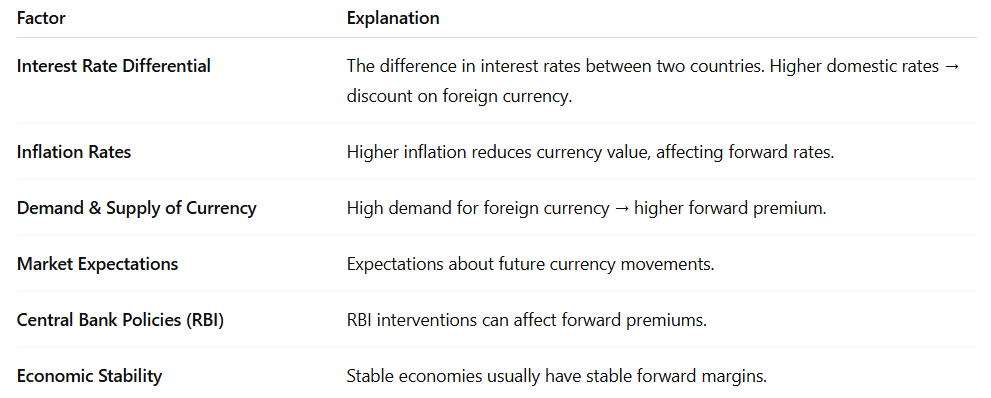
Factors Determining Forward Margin
Summary Table
Merchant Rates
Merchant rates are the foreign exchange rates quoted by banks to their customers (merchants/importers/exporters) for buying or selling foreign currencies.
Basis of Merchant Rates
Merchant rates are based on:
Types of Buying and Selling Rates
Banks quote different rates for buying and selling foreign exchange, depending on the purpose and timing.
Types of Buying Rates
Types of Selling Rates
Ready Rates Based on Cross Rates
Cross Rates: A cross rate is the exchange rate between two currencies derived from a third common currency (usually USD).
Example of Cross Rate: You want INR/GBP rate, but only INR/USD and USD/GBP are available.
Ready Rates: Ready (Spot) Rates for currencies not directly quoted (e.g., INR/EUR) are calculated using cross rates.
Example
- INR/USD = ₹82
- USD/GBP = 0.75
- Then, INR/GBP = ₹82 / 0.75 ≈ ₹109.33
Summary Table
Forward Exchange Contract
A Forward Exchange Contract is an agreement between a bank and a customer to buy or sell foreign currency at a predetermined rate on a future date.
It protects against foreign exchange risk due to currency rate fluctuations.
Types of Forward Contracts
Difference Between Fixed and Option Forward Contracts
Calculation of Fixed and Option Forward Rates
Formula:
- Add Forward Margin if currency is at a premium.
- Subtract Forward Margin if currency is at a discount.
Option Forward Rate Calculation: For option contracts, banks use the forward margin for the last date of the option period.
- Spot rate = ₹82/USD
- 1-month premium = ₹0.50
- 2-month premium = ₹0.80
- → 1–2 month option forward rate = ₹82 + ₹0.80 = ₹82.80/USD
Inter-Bank Deals
- Managing liquidity
- Covering customer positions
- Hedging risks
Types
Execution of Forward Contracts
Steps
- Agreement Signed: Bank and customer sign a forward contract specifying rate, amount, date.
- Booking the Deal: Bank books the deal in its forex system and commits the rate.
- Covering Position: Bank may cover the contract through inter-bank forward deals.
Settlement on Due Date
- Customer delivers the agreed amount.
- Bank delivers currency as per contract rate.
Cancellation and Extension
- If the customer fails to fulfill the contract:
- Bank cancels the contract and recovers loss/gives profit.
- Contract can be extended with revised forward rate.