Introduction to Commodity Markets
Commodity Markets
A commodity market is a platform where raw materials or primary products like gold, crude oil, wheat, cotton, etc., are bought and sold. These markets facilitate trading in physical form or through derivative contracts (futures & options).
History of Commodity Trading
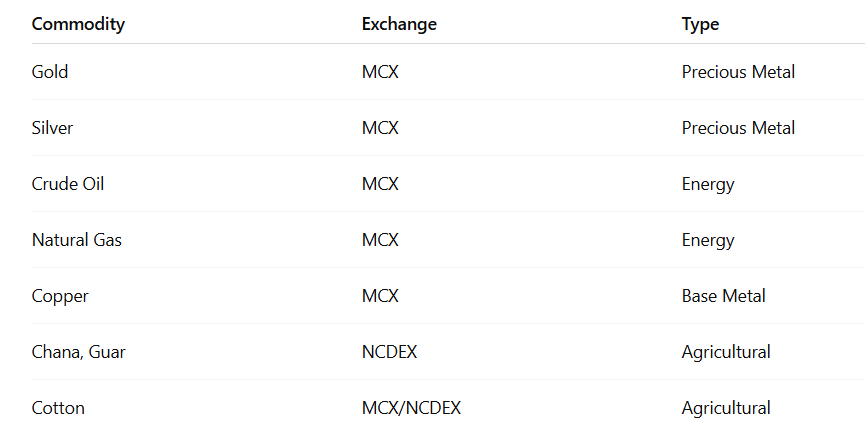
Major Commodities Traded in Indian Derivatives Exchanges
India’s commodity derivatives market is regulated by SEBI and operated through exchanges like:
- MCX – Multi Commodity Exchange (Mumbai)
- NCDEX – National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange (Mumbai)
- ICEX, NMCE (merged with ICEX)
Categories of Commodities Traded
Most Actively Traded Commodities in India (Derivatives)
Purpose of Commodity Derivatives Market
Summary Table
Participants in Commodity Derivative Markets
Commodity derivative markets include a variety of players with different motives: hedging, speculation, arbitrage, or investment.
Types of Participants
Commodity Market Indices
Commodity indices are benchmarks that measure the price movement of a basket of commodities (like crude oil, gold, cotton, etc.).
They are used for:
- Market tracking
- Benchmarking fund performance
- Index-based investing
- Derivative contracts (Index futures/options)
Popular Commodity Indices in India
Example: MCX iCOMDEX
MCX has launched multiple indices under iCOMDEX:
- iCOMDEX Bullion (Gold + Silver)
- iCOMDEX Base Metals (Copper, Aluminium, etc.)
- iCOMDEX Energy (Crude oil + Natural gas)
- iCOMDEX Composite (all categories combined)
These indices help:
- Track sectoral commodity trends
- Develop index-based futures
Commodity Futures
A commodity future is a standardized agreement to buy or sell a specific quantity of a commodity at a predetermined price on a future date, traded on an exchange.
These are regulated by SEBI in India and traded on MCX, NCDEX, etc.
Features of Commodity Futures
Example: A farmer expects wheat prices to fall in 3 months.
- He sells wheat futures now to lock a higher price.
- At expiry, if market price is lower, he gains in futures, offsetting loss in spot market.
Summary Table
Commodity Options
A Commodity Option is a derivative contract that gives the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of a commodity at a predetermined price before or on a future date.
Traded on exchanges like MCX in India under SEBI regulations.
Types of Commodity Options
Examples
- Gold Options
- Silver Options
- Crude Oil Options
- Agri-based options (Cotton Seed Oilcake, etc.)
Uses of Commodity Derivatives
Commodity derivatives like futures and options help in various ways:
A. Hedging: Used by producers, consumers, and traders to protect against price risks. Example: A jeweller afraid of gold price rise buys a Gold Call Option to fix the price.
B. Speculation: Used by traders who take risk to earn profits based on price movements. Example: A trader expects crude oil prices to rise → buys Crude Oil Futures.
C. Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences in different markets (spot vs future, or across exchanges). Example: Gold in spot market is ₹60,000, but futures are trading at ₹61,000.
Arbitrageur buys in spot & sells in futures to earn risk-free profit.