Unit 5: Exchange Risk
Exchange Risk vs Exchange Exposure
Simple Difference
Risk = Uncertainty of loss. Exposure = The extent to which a company or person is vulnerable to risk.
Example: An Indian company has to pay $10,000 in 30 days. If USD/INR moves unfavorably, it faces exchange risk. The $10,000 is the exchange exposure.
Transaction Exposure
Example: You sold goods to a US buyer and will receive $20,000 in 2 months. If the USD weakens, you will receive fewer INR. This is transaction exposure.
Managing Transaction Exposure
There are two main strategies
- Internal Hedging (e.g., leading/lagging payments, netting)
- External Hedging (using financial instruments)
External Hedge: Forward Contract Hedge
Example: An Indian importer agrees to buy $50,000 worth of goods in 3 months. He fears the USD may appreciate. He enters a forward contract to buy $50,000 at ₹84/USD. Even if the market moves to ₹86/USD, he still pays only ₹84/USD → loss avoided.
Summary Table
Money Market Hedge (External Hedge)
Risk Avoided: Any USD appreciation is irrelevant — payment is pre-arranged.
Hedging with Futures and Options
A. Futures Contract Hedge
Example: You must pay $10,000 in 3 months. You buy USD futures today at ₹84/USD. Even if the rate becomes ₹86, you gain ₹2 in the futures market, offsetting the higher cost.
B. Options Contract Hedge
Example: You expect to receive $10,000. You buy a put option at ₹84/USD. If rate falls to ₹82/USD, you sell at ₹84, avoiding loss. If rate is ₹85, you ignore the option and sell at market rate.
Internal Hedge (Natural Hedging Techniques)
Examples: Leading: Pay early if foreign currency is expected to rise. Lagging: Delay payment if currency is expected to fall. Netting: A company has to pay $10,000 and receive $8,000 → net exposure = $2,000 only.
Translation Exposure (Accounting Exposure)
Example: A US-based company has a UK subsidiary. The subsidiary's GBP profits must be converted to USD for reporting. If GBP weakens, USD profit appears lower → translation loss.
Key Features of Translation Exposure
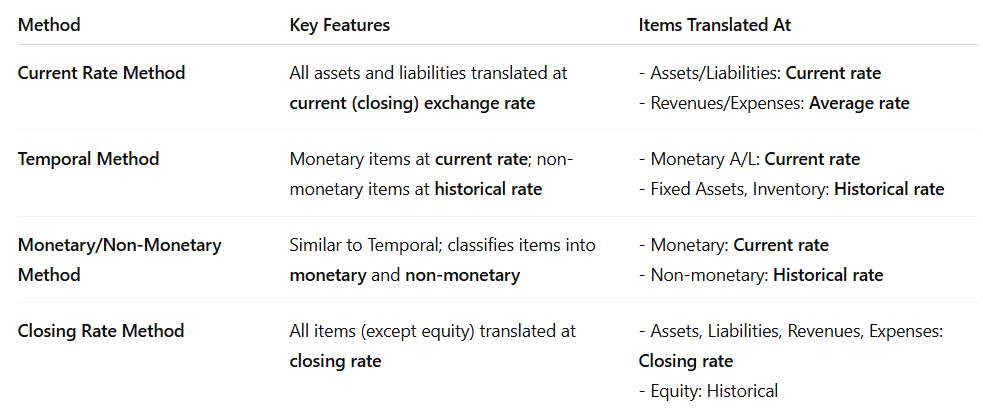
Methods of Translation
Used to convert foreign subsidiary’s financial statements into parent company’s currency for reporting.